17 Mar What is GNSS?
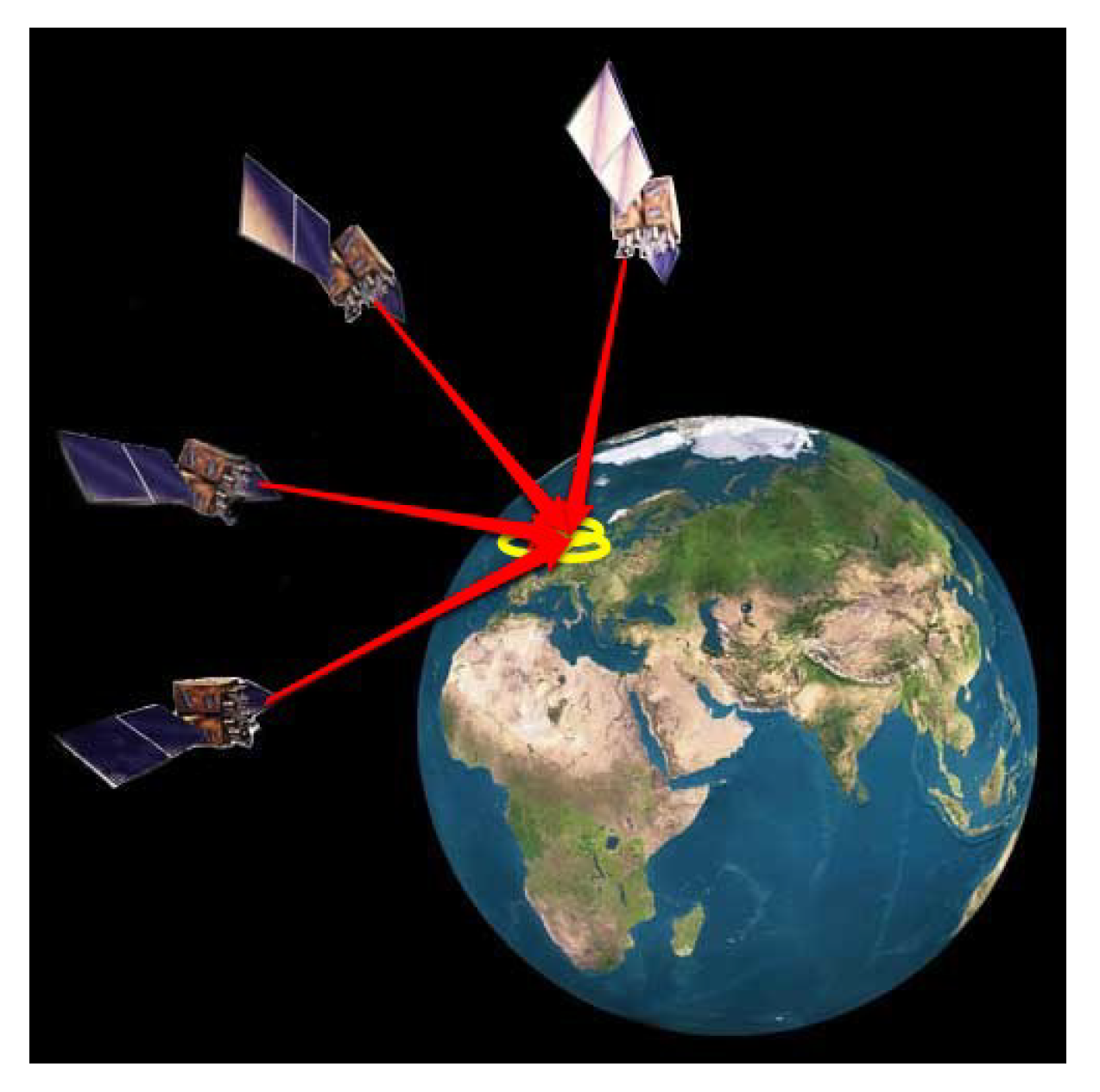
In today’s fast-paced world, technology is constantly evolving, and one such technology that has revolutionized the way we navigate is GNSS. GNSS, short for Global Navigation Satellite System, is a network of satellites that transmit signals that enable users to determine their location and time, irrespective of their geographical location.
GNSS systems are used in a variety of applications, including transportation, aviation, marine navigation, and precision agriculture. With its widespread usage, it has become an integral part of modern society. Despite its widespread use, many people are unaware of what GNSS is and how it works.
GNSS operates through a network of satellites that are placed in orbit around the Earth. These satellites transmit signals to ground-based receivers, which then determine the user’s location by triangulation. The accuracy of the location depends on the number of satellites that the receiver can detect and the quality of the signals received.
The most commonly used GNSS systems are the US-based GPS (Global Positioning System), the Russian GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System), the European Galileo, and the Chinese BeiDou. All these systems operate on the same principles, but they have slight variations in their signals and coverage areas.
GNSS has become an essential tool for many industries, especially those that rely on precise location data, such as transportation and logistics. For example, it is used in autonomous vehicles to navigate, and in aviation to guide aircraft during takeoff, landing, and in-flight. It also helps farmers to optimize their crop yields by providing them with accurate data on soil moisture and nutrient levels.
Despite its benefits, GNSS is not without its challenges. One of the main challenges is the susceptibility of the signals to interference, which can cause inaccuracies in the location data. This issue is being addressed through the development of new technology and protocols to ensure the integrity of the GNSS signals.
In conclusion, GNSS has become an essential part of modern life, providing accurate location and time information to users across the world. With its widespread use and constant evolution, it will continue to play a vital role in shaping the future of transportation, logistics, and other industries that rely on precise location data.
GNSS, short for Global Navigation Satellite System, is a network of satellites that transmit signals that enable users to determine their location and time, irrespective of their geographical location.



